Bloomberg
Updated: June 18th, 2020
A last ditch attempt to resolve a decade-long dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over a huge new hydropower dam on the Nile has failed, raising the stakes in what – for all the public focus on technical issues – is a tussle for control over the region’s most important water source.
The talks appear to have faltered over a recurring issue: Ethiopia’s refusal to accept a permanent, minimum volume of water that the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, or GERD, should release downstream in the event of severe drought.
What happens next remains uncertain. Both Ethiopia and Sudan – a mutual neighbor that took part in the talks – said that progress had been made and left the door open to further negotiation. Yet the stakes in a region acutely vulnerable to the impact of climate change are disconcertingly clear.
Ethiopia has threatened to start filling the dam’s reservoir when the rainy season begins in July, with or without a deal, a step Egypt considers both unacceptable and illegal. In a statement late Wednesday, Egypt’s irrigation ministry accused Ethiopia of refusing to accept any effective drought provision or legally binding commitments, or even to refer the talks to the three prime ministers in an effort to break the deadlock. Ethiopia was demanding “an absolute right” to build further dams behind the GERD, the ministry said.
Egypt’s Foreign Minister Sameh Shoukry threatened on Monday to call for United Nations Security Council intervention to protect “international peace and security” if no agreement was reached. A day later his Ethiopian opposite, Gedu Andargachew, accused Egypt of “acting as if it is the sole owner of the Nile waters.”
Egyptian billionaire Naguib Sawiris even warned of a water war. “We will never allow any country to starve us, if Ethiopia doesn’t come to reason, we the Egyptian people will be the first to call for war,” he said in a tweet earlier this week.
Although both sides have played down the prospect of military conflict, they have occasionally rattled sabers and concern at the potential for escalation helped draw the U.S. and World Bank into the negotiating process last year. When that attempt floundered in February, the European Union and South Africa, as chair of the African Union, joined in.
“This is all about control,” said Asfaw Beyene, a professor of mechanical engineering at San Diego State University, California, whose work Egypt cited in support of a May 1 report to the UN. The so-called aide memoire argued that the GERD and its 74 billion cubic meter reservoir are so vastly oversized relative to the power they will produce that it “raises questions about the true purpose of the dam.”
National Survival
Egypt’s concern is that once the dam’s sluices can control the Nile’s flow, Ethiopia could in times of drought say “I am not releasing water, I need it,” or dictate how the water released is used, says Asfaw. Yet he backs Ethiopia’s claims that once filled, the dam won’t significantly affect downstream supplies. He also agrees with their argument that climate change could render unsustainable any water guarantees given to Egypt.
Both sides describe the future of the hydropower dam that will generate as much as 15.7 gigawatts of electricity per year as a matter of national survival. Egypt relies on the Nile for as much as 97% of an already strained water supply. Ethiopia says the dam is vital for development, because it would increase the nation’s power generation by about 150% at a time when more than half the population have no access to electricity.
—
UPDATE: Ethiopian Army Official Says Country Will Defend Itself Over Dam (AP)
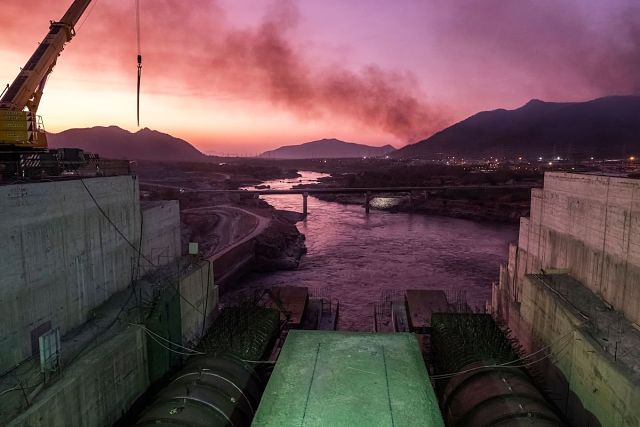

A general view of the Blue Nile river as it passes through the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), near Guba in Ethiopia. (Getty Images)
By ELIAS MESERET
Updated: June 12th, 2020
ADDIS ABABA, Ethiopia (AP) — Ethiopia’s deputy army chief on Friday said his country will strongly defend itself and will not negotiate its sovereignty over the disputed $4.6 billion Nile dam that has caused tensions with Egypt.
“Egyptians and the rest of the world know too well how we conduct war whenever it comes,” Gen. Birhanu Jula said in an interview with the state-owned Addis Zemen newspaper, adding that Egyptian leaders’ “distorted narrative” on Africa’s largest hydroelectric dam is attracting enemies.
He accused Egypt of using its weapons to “threaten and tell other countries not to touch the shared water” and said “the way forward should be cooperation in a fair manner.”
He spoke amid renewed talks among Ethiopian, Sudanese and Egyptian water and irrigation ministers after months of deadlock. Ethiopia wants to begin filling the dam’s reservoir in the coming weeks, but Egypt worries a rapid filling will take too much of the water it says its people need to survive. Sudan, caught between the competing interests, pushed the two sides to resume discussions.
The general’s comments were a stark contrast to Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed’s remarks to lawmakers earlier this week that diplomacy should take center stage to resolve outstanding issues.
“We don’t want to hurt anyone else, and at the same time it will be difficult for us to accept the notion that we don’t deserve to have electricity,” the Nobel Peace Prize laureate said. “We are tired of begging others while 70% of our population is young. This has to change.”
Talks on the dam have struggled. Egypt’s Irrigation Ministry on Wednesday called for Ethiopia to “clearly declare that it had no intention of unilaterally filling the reservoir” and that a deal prepared by the U.S. and the World Bank in February serves as the starting point of the resumed negotiations.
Ethiopia refused to sign that deal and accused the U.S. of siding with Egypt.
Egypt said that in Tuesday’s talks, Ethiopia showed it wanted to re-discuss “all issues” including “all timetables and figures” negotiated in the U.S.-brokered talks.
President Abdel-Fattah el-Sissi discussed the latest negotiations in a phone call with President Donald Trump on Wednesday, el-Sissi’s office said, without elaborating.
Egypt’s National Security Council, the highest body that makes decisions in high-profile security matters in the country, has accused Ethiopia of “buying time” and seeking to begin filling the dam’s reservoir in July without reaching a deal with Egypt and Sudan.
—
Ethiopia Seeks to Limit Outsiders’ Role in Nile Dam Talks (AFP)
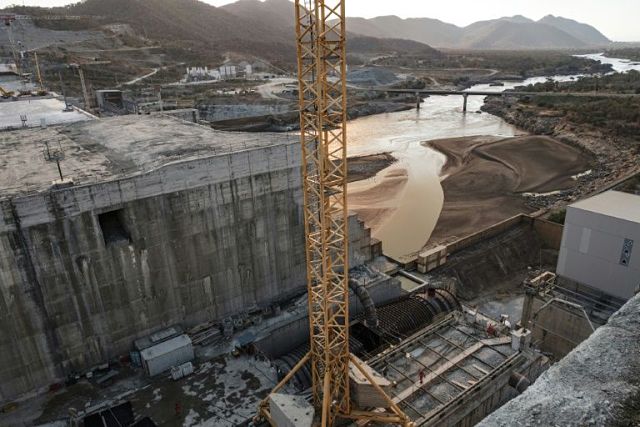

Ethiopia sees the dam as essential for its electrification and development, while Sudan and Egypt see it as a threat to essential water supplies (AFP Photo)
Updated: June 11th, 2020
Addis Ababa (AFP) – Ethiopia said Thursday it wants to limit the role of outside parties in revived talks over its Nile River mega-dam, a sign of lingering frustration over a failed attempt by the US to broker a deal earlier this year.
The Grand Ethiopia Renaissance Dam has been a source of tension in the Nile River basin ever since Ethiopia broke ground on it nearly a decade ago.
Ethiopia sees the dam as essential for its electrification and development, while Sudan and Egypt see it as a threat to essential water supplies.
The US Treasury Department stepped in last year after Egyptian President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi put in a request to his ally US President Donald Trump.
But the process ran aground after the Treasury Department urged Ethiopia to sign a deal that Egypt backed as “fair and balanced”.
Ethiopia denied a deal had been reached and accused Washington of being “undiplomatic” and playing favourites.
On Tuesday Ethiopia, Egypt and Sudan resumed talks via videoconference with representatives of the United States, the European Union and South Africa taking part.
The talks resumed Wednesday and were expected to pick up again Thursday.
In a statement aired Thursday by state-affiliated media, Ethiopia’s water ministry said the role of the outside parties should not “exceed that of observing the negotiation and sharing good practices when jointly requested by the three countries.”
The statement also criticised Egypt for detailing its grievances over the dam in a May letter to the UN Security Council — a move it described as a bad faith attempt to “exert external diplomatic pressure”.
Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed reiterated Monday that his country plans to begin filling the dam’s reservoir in the coming weeks, giving the latest talks heightened urgency.
The short window makes it “more necessary than ever that concessions are made so a deal can be struck that will ease potentially dangerous tensions,” said William Davison of the International Crisis Group, a conflict prevention organisation.
One solution could involve Ethiopia “proposing a detailed cooperative annual drought-management scheme that takes Egypt and Sudan’s concerns into account, but does not unacceptably constrain the dam’s potential,” he said.
The EU sees the resumption of talks as “an important opportunity to restore confidence among the parties, build on the good progress achieved and agree on a mutually beneficial solution,” said spokeswoman Virginie Battu-Henriksson.
“Especially in this time of global crisis, it is important to appease tensions and find pragmatic solutions,” she said.
—